Symptoms
The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of conditions that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy immune systems. Most of these conditions are infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites that are normally controlled by the elements of the immune system that HIV damages. Opportunistic infections are common in people with AIDS.[10] HIV affects nearly every organ system. People with AIDS also have an increased risk of developing various cancers such as Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer and cancers of the immune system known as lymphomas. Additionally, people with AIDS often have systemic symptoms of infection like fevers, sweats (particularly at night), swollen glands, chills, weakness, and weight loss.[11][12] The specific opportunistic infections that AIDS patients develop depend in part on the prevalence of these infections in the geographic area in which the patient lives.
Pulmonary infections

Pneumocystis pneumonia (originally known as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, and still abbreviated as PCP, which now stands for Pneumocystis pneumonia) is relatively rare in healthy, immunocompetent people, but common among HIV-infected individuals. It is caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii. Before the advent of effective diagnosis, treatment and routine prophylaxis in Western countries, it was a common immediate cause of death. In developing countries, it is still one of the first indications of AIDS in untested individuals, although it does not generally occur unless the CD4 count is less than 200 cells per µL of blood.[13]
Tuberculosis (TB) is unique among infections associated with HIV because it is transmissible to immunocompetent people via the respiratory route, is easily treatable once identified, may occur in early-stage HIV disease, and is preventable with drug therapy. However, multidrug resistance is a potentially serious problem. Even though its incidence has declined because of the use of directly observed therapy and other improved practices in Western countries, this is not the case in developing countries where HIV is most prevalent. In early-stage HIV infection (CD4 count >300 cells per µL), TB typically presents as a pulmonary disease. In advanced HIV infection, TB often presents atypically with extrapulmonary (systemic) disease a common feature. Symptoms are usually constitutional and are not localized to one particular site, often affecting bone marrow, bone, urinary and gastrointestinal tracts, liver, regional lymph nodes, and the central nervous system.[14]
Gastrointestinal infections
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the lining of the lower end of the esophagus (gullet or swallowing tube leading to the stomach). In HIV infected individuals, this is normally due to fungal (candidiasis) or viral (herpes simplex-1 or cytomegalovirus) infections. In rare cases, it could be due to mycobacteria.[15]
Unexplained chronic diarrhea in HIV infection is due to many possible causes, including common bacterial (Salmonella, Shigella, Listeria or Campylobacter) and parasitic infections; and uncommon opportunistic infections such as cryptosporidiosis, microsporidiosis, Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) and viruses,[16] astrovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus and cytomegalovirus, (the latter as a course of colitis). In some cases, diarrhea may be a side effect of several drugs used to treat HIV, or it may simply accompany HIV infection, particularly during primary HIV infection. It may also be a side effect of antibiotics used to treat bacterial causes of diarrhea (common for Clostridium difficile). In the later stages of HIV infection, diarrhea is thought to be a reflection of changes in the way the intestinal tract absorbs nutrients, and may be an important component of HIV-related wasting.[17]
Neurological and psychiatric involvement
HIV infection may lead to a variety of neuropsychiatric sequelae, either by infection of the now susceptible nervous system by organisms, or as a direct consequence of the illness itself.
Toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by the single-celled parasite called Toxoplasma gondii; it usually infects the brain, causing toxoplasma encephalitis, but it can also infect and cause disease in the eyes and lungs.[18] Cryptococcal meningitis is an infection of the meninx (the membrane covering the brain and spinal cord) by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. It can cause fevers, headache, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. Patients may also develop seizures and confusion; left untreated, it can be lethal.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a demyelinating disease, in which the gradual destruction of the myelin sheath covering the axons of nerve cells impairs the transmission of nerve impulses. It is caused by a virus called JC virus which occurs in 70% of the population in latent form, causing disease only when the immune system has been severely weakened, as is the case for AIDS patients. It progresses rapidly, usually causing death within months of diagnosis.[19]
AIDS dementia complex (ADC) is a metabolic encephalopathy induced by HIV infection and fueled by immune activation of HIV infected brain macrophages and microglia. These cells are productively infected by HIV and secrete neurotoxins of both host and viral origin.[20] Specific neurological impairments are manifested by cognitive, behavioral, and motor abnormalities that occur after years of HIV infection and are associated with low CD4+ T cell levels and high plasma viral loads. Prevalence is 10–20% in Western countries[21] but only 1–2% of HIV infections in India.[22][23] This difference is possibly due to the HIV subtype in India. AIDS related mania is sometimes seen in patients with advanced HIV illness; it presents with more irritability and cognitive impairment and less euphoria than a manic episode associated with true bipolar disorder. Unlike the latter condition, it may have a more chronic course. This syndrome is less often seen with the advent of multi-drug therapy.
Tumors and malignancies
Patients with HIV infection have substantially increased incidence of several cancers. This is primarily due to co-infection with an oncogenic DNA virus, especially Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), and human papillomavirus (HPV).[24][25]
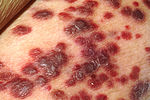
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is the most common tumor in HIV-infected patients. The appearance of this tumor in young homosexual men in 1981 was one of the first signals of the AIDS epidemic. Caused by a gammaherpes virus called Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV), it often appears as purplish nodules on the skin, but can affect other organs, especially the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs.
High-grade B cell lymphomas such as Burkitt's lymphoma, Burkitt's-like lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and primary central nervous system lymphoma present more often in HIV-infected patients. These particular cancers often foreshadow a poor prognosis. In some cases these lymphomas are AIDS-defining. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) or KSHV cause many of these lymphomas.
Cervical cancer in HIV-infected women is considered AIDS-defining. It is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV).[26]
In addition to the AIDS-defining tumors listed above, HIV-infected patients are at increased risk of certain other tumors, such as Hodgkin's disease and anal and rectal carcinomas. However, the incidence of many common tumors, such as breast cancer or colon cancer, does not increase in HIV-infected patients. In areas where HAART is extensively used to treat AIDS, the incidence of many AIDS-related malignancies has decreased, but at the same time malignant cancers overall have become the most common cause of death of HIV-infected patients.[27]
Other opportunistic infections
AIDS patients often develop opportunistic infections that present with non-specific symptoms, especially low-grade fevers and weight loss. These include infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and cytomegalovirus (CMV). CMV can cause colitis, as described above, and CMV retinitis can cause blindness. Penicilliosis due to Penicillium marneffei is now the third most common opportunistic infection (after extrapulmonary tuberculosis and cryptococcosis) in HIV-positive individuals within the endemic area of Southeast Asia.[28]
Cause
- For more details on this topic, see HIV.
AIDS is the most severe acceleration of infection with HIV. HIV is a retrovirus that primarily infects vital organs of the human immune system such as CD4+ T cells (a subset of T cells), macrophages and dendritic cells. It directly and indirectly destroys CD4+ T cells.[29] Once HIV has killed so many CD4+ T cells that there are fewer than 200 of these cells per microliter (µL) of blood, cellular immunity is lost. Acute HIV infection progresses over time to clinical latent HIV infection and then to early symptomatic HIV infection and later to AIDS, which is identified either on the basis of the amount of CD4+ T cells remaining in the blood, and/or the presence of certain infections, as noted above.[30]
In the absence of antiretroviral therapy, the median time of progression from HIV infection to AIDS is nine to ten years, and the median survival time after developing AIDS is only 9.2 months.[31] However, the rate of clinical disease progression varies widely between individuals, from two weeks up to 20 years. Many factors affect the rate of progression. These include factors that influence the body's ability to defend against HIV such as the infected person's general immune function.[32][33] Older people have weaker immune systems, and therefore have a greater risk of rapid disease progression than younger people. Poor access to health care and the existence of coexisting infections such as tuberculosis also may predispose people to faster disease progression.[31][34][35] The infected person's genetic inheritance plays an important role and some people are resistant to certain strains of HIV. An example of this is people with the homozygous CCR5-Δ32 variation are resistant to infection with certain strains of HIV.[36] HIV is genetically variable and exists as different strains, which cause different rates of clinical disease progression.[37][38][39]
Sexual transmission
Sexual transmission occurs with the contact between sexual secretions of one person with the rectal, genital or oral mucous membranes of another. Unprotected receptive sexual acts are riskier than unprotected insertive sexual acts, and the risk for transmitting HIV through unprotected anal intercourse is greater than the risk from vaginal intercourse or oral sex. However, oral sex is not entirely safe, as HIV can be transmitted through both insertive and receptive oral sex.[40][41] Sexual assault greatly increases the risk of HIV transmission as protection is rarely employed and physical trauma to the vagina frequently occurs, facilitating the transmission of HIV.[42]
Other sexually transmitted infections (STI) increase the risk of HIV transmission and infection, because they cause the disruption of the normal epithelial barrier by genital ulceration and/or microulceration; and by accumulation of pools of HIV-susceptible or HIV-infected cells (lymphocytes and macrophages) in semen and vaginal secretions. Epidemiological studies from sub-Saharan Africa, Europe and North America suggest that genital ulcers, such as those caused by syphilis and/or chancroid, increase the risk of becoming infected with HIV by about four-fold. There is also a significant although lesser increase in risk from STIs such as gonorrhea, Chlamydial infection and trichomoniasis, which all cause local accumulations of lymphocytes and macrophages.[43]
Transmission of HIV depends on the infectiousness of the index case and the susceptibility of the uninfected partner. Infectivity seems to vary during the course of illness and is not constant between individuals. An undetectable plasma viral load does not necessarily indicate a low viral load in the seminal liquid or genital secretions. However, each 10-fold increase in the level of HIV in the blood is associated with an 81% increased rate of HIV transmission.[43][44] Women are more susceptible to HIV-1 infection due to hormonal changes, vaginal microbial ecology and physiology, and a higher prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases.[45][46] People who have been infected with one strain of HIV can still be infected later on in their lives by other, more virulent strains.
Infection is unlikely in a single encounter. High rates of infection have been linked to a pattern of overlapping long-term romantic relationships. This allows the virus to quickly spread to multiple partners who in turn infect their partners. A pattern of serial monogamy or occasional casual encounters is associated with lower rates of infection.[47]
HIV spreads readily through heterosexual sex in Africa, but less so elsewhere. One possibility being researched is that schistosomiasis, which affects up to 50 per cent of women in parts of Africa, damages the lining of the vagina.[48][49]
Exposure to blood-borne pathogens
This transmission route is particularly relevant to intravenous drug users, hemophiliacs and recipients of blood transfusions and blood products. Sharing and reusing syringes contaminated with HIV-infected blood represents a major risk for infection with HIV. Needle sharing is the cause of one third of all new HIV-infections in North America, China, and Eastern Europe. The risk of being infected with HIV from a single prick with a needle that has been used on an HIV-infected person is thought to be about 1 in 150 (see table above). Post-exposure prophylaxis with anti-HIV drugs can further reduce this risk.[50] This route can also affect people who give and receive tattoos and piercings. Universal precautions are frequently not followed in both sub-Saharan Africa and much of Asia because of both a shortage of supplies and inadequate training. The WHO estimates that approximately 2.5% of all HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa are transmitted through unsafe healthcare injections.[51] Because of this, the United Nations General Assembly has urged the nations of the world to implement precautions to prevent HIV transmission by health workers.[52]
The risk of transmitting HIV to blood transfusion recipients is extremely low in developed countries where improved donor selection and HIV screening is performed. However, according to the WHO, the overwhelming majority of the world's population does not have access to safe blood and between 5% and 10% of the world's HIV infections come from transfusion of infected blood and blood products.[53]
Perinatal transmission
The transmission of the virus from the mother to the child can occur in utero during the last weeks of pregnancy and at childbirth. In the absence of treatment, the transmission rate between a mother and her child during pregnancy, labor and delivery is 25%. However, when the mother takes antiretroviral therapy and gives birth by caesarean section, the rate of transmission is just 1%.[54] The risk of infection is influenced by the viral load of the mother at birth, with the higher the viral load, the higher the risk. Breastfeeding also increases the risk of transmission by about 4 %.[55]
Misconceptions
A number of misconceptions have arisen surrounding HIV/AIDS. Three of the most common are that AIDS can spread through casual contact, that sexual intercourse with a virgin will cure AIDS, and that HIV can infect only homosexual men and drug users. Other misconceptions are that any act of anal intercourse between gay men can lead to AIDS infection, and that open discussion of homosexuality and HIV in schools will lead to increased rates of homosexuality and AIDS.[56]
Pathophysiology
| This section may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. Please improve this article if you can. (April 2008) |
The pathophysiology of AIDS is complex, as is the case with all syndromes.[57] Ultimately, HIV causes AIDS by depleting CD4+ T helper lymphocytes. This weakens the immune system and allows opportunistic infections. T lymphocytes are essential to the immune response and without them, the body cannot fight infections or kill cancerous cells. The mechanism of CD4+ T cell depletion differs in the acute and chronic phases.[58] During the acute phase, HIV-induced cell lysis and killing of infected cells by cytotoxic T cells accounts for CD4+ T cell depletion, although apoptosis may also be a factor. During the chronic phase, the consequences of generalized immune activation coupled with the gradual loss of the ability of the immune system to generate new T cells appear to account for the slow decline in CD4+ T cell numbers.
Although the symptoms of immune deficiency characteristic of AIDS do not appear for years after a person is infected, the bulk of CD4+ T cell loss occurs during the first weeks of infection, especially in the intestinal mucosa, which harbors the majority of the lymphocytes found in the body. [59] The reason for the preferential loss of mucosal CD4+ T cells is that a majority of mucosal CD4+ T cells express the CCR5 coreceptor, whereas a small fraction of CD4+ T cells in the bloodstream do so.[60] HIV seeks out and destroys CCR5 expressing CD4+ cells during acute infection. A vigorous immune response eventually controls the infection and initiates the clinically latent phase. However, CD4+ T cells in mucosal tissues remain depleted throughout the infection, although enough remain to initially ward off life-threatening infections.
Continuous HIV replication results in a state of generalized immune activation persisting throughout the chronic phase. [61] Immune activation, which is reflected by the increased activation state of immune cells and release of proinflammatory cytokines, results from the activity of several HIV gene products and the immune response to ongoing HIV replication. Another cause is the breakdown of the immune surveillance system of the mucosal barrier caused by the depletion of mucosal CD4+ T cells during the acute phase of disease.[62] This results in the systemic exposure of the immune system to microbial components of the gut’s normal flora, which in a healthy person is kept in check by the mucosal immune system. The activation and proliferation of T cells that results from immune activation provides fresh targets for HIV infection. However, direct killing by HIV alone cannot account for the observed depletion of CD4+ T cells since only 0.01-0.10% of CD4+ T cells in the blood are infected. A major cause of CD4+ T cell loss appears to result from their heightened susceptibility to apoptosis when the immune system remains activated. Although new T cells are continuously produced by the thymus to replace the ones lost, the regenerative capacity of the thymus is slowly destroyed by direct infection of its thymocytes by HIV. Eventually, the minimal number of CD4+ T cells necessary to maintain a sufficient immune response is lost, leading to AIDS
Cells affected
The virus, entering through which ever route, acts primarily on the following cells:[63]
- Lymphoreticular system:
- CD4+ T-Helper cells
- CD4+ Macrophages
- CD4+ Monocytes
- B-lymphocytes
- Certain endothelial cells
- Central nervous system:
- Microglia of the nervous system
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Neurones - indirectly by the action of cytokines and the gp-120
The effect
The virus has cytopathic effects but how it does it is still not quite clear. It can remain inactive in these cells for long periods, though. This effect is hypothesized to be due to the CD4-gp120 interaction.[64]
- The most prominent effect of the HIV virus is its T-helper cell suppression and lysis. The cell is simply killed off or deranged to the point of being function-less (they do not respond to foreign antigens). The infected B-cells can not produce enough antibodies either. Thus the immune system collapses leading to the familiar AIDS complications, like infections and neoplasms (vide supra).
- Infection of the cells of the CNS cause acute aseptic meningitis, subacute encephalitis, vacuolar myelopathy and peripheral neuropathy. Later it leads to even AIDS dementia complex.
- The CD4-gp120 interaction (vide supra) is also permissive to other viruses like Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis virus, Herpes simplex virus, etc. These viruses lead to further cell damage i.e. cytopathy.
Molecular basis
For details, see:
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of AIDS in a person infected with HIV is based on the presence of certain signs or symptoms. Since June 5, 1981, many definitions have been developed for epidemiological surveillance such as the Bangui definition and the 1994 expanded World Health Organization AIDS case definition. However, clinical staging of patients was not an intended use for these systems as they are neither sensitive, nor specific. In developing countries, the World Health Organization staging system for HIV infection and disease, using clinical and laboratory data, is used and in developed countries, the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Classification System is used.
WHO disease staging system
In 1990, the World Health Organization (WHO) grouped these infections and conditions together by introducing a staging system for patients infected with HIV-1.[65] An update took place in September 2005. Most of these conditions are opportunistic infections that are easily treatable in healthy people.
- Stage I: HIV infection is asymptomatic and not categorized as AIDS
- Stage II: includes minor mucocutaneous manifestations and recurrent upper respiratory tract infections
- Stage III: includes unexplained chronic diarrhea for longer than a month, severe bacterial infections and pulmonary tuberculosis
- Stage IV: includes toxoplasmosis of the brain, candidiasis of the esophagus, trachea, bronchi or lungs and Kaposi's sarcoma; these diseases are indicators of AIDS.
CDC classification system
There are two main definitions for AIDS, both produced by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The older definition is to referring to AIDS using the diseases that were associated with it, for example, lymphadenopathy, the disease after which the discoverers of HIV originally named the virus.[66][67] In 1993, the CDC expanded their definition of AIDS to include all HIV positive people with a CD4+ T cell count below 200 per µL of blood or 14% of all lymphocytes.[68] The majority of new AIDS cases in developed countries use either this definition or the pre-1993 CDC definition. The AIDS diagnosis still stands even if, after treatment, the CD4+ T cell count rises to above 200 per µL of blood or other AIDS-defining illnesses are cured.
HIV test
Many people are unaware that they are infected with HIV.[69] Less than 1% of the sexually active urban population in Africa has been tested, and this proportion is even lower in rural populations. Furthermore, only 0.5% of pregnant women attending urban health facilities are counseled, tested or receive their test results. Again, this proportion is even lower in rural health facilities.[69] Therefore, donor blood and blood products used in medicine and medical research are screened for HIV.
HIV tests are usually performed on venous blood. Many laboratories use fourth generation screening tests which detect anti-HIV antibody (IgG and IgM) and the HIV p24 antigen. The detection of HIV antibody or antigen in a patient previously known to be negative is evidence of HIV infection. Individuals whose first specimen indicates evidence of HIV infection will have a repeat test on a second blood sample to confirm the results. The window period (the time between initial infection and the development of detectable antibodies against the infection) can vary since it can take 3–6 months to seroconvert and to test positive. Detection of the virus using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) during the window period is possible, and evidence suggests that an infection may often be detected earlier than when using a fourth generation EIA screening test. Positive results obtained by PCR are confirmed by antibody tests.[70] Routinely used HIV tests for infection in neonates, born to HIV-positive mothers, have no value because of the presence of maternal antibody to HIV in the child's blood. HIV infection can only be diagnosed by PCR, testing for HIV pro-viral DNA in the children's lymphocytes.[71]



No comments:
Post a Comment